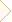What are the cases of subwoofers. Their description and characteristics
This article will cover 3 basic types of enclosures that are used in subwoofers (and in other speaker systems). But first, some information about what the box is meant for and what functions it carries. The acoustic head makes a sound not necessarily forward itself, but also back, and the front and rear sound waves will be inverse in phase. That is why the term “acoustic closure” was coined, in which the waves on both sides of the diffuser are superimposed and, if they are opposite in phase, are canceled with each other. Ideally, this should not be felt in any way, but in practice the sound will be far from conceived. The box in the speaker system makes it possible to remove such a closure and give the sound the necessary properties in terms of frequency and power. At 130.com.ua you can buy a cabinet subwoofer in Kharkov, Odessa, Kiev with delivery in Ukraine.
There are 3 main types of housing design: a closed box, a phase inverter and a bandpass. Consider each of them in more detail.
Sealed box
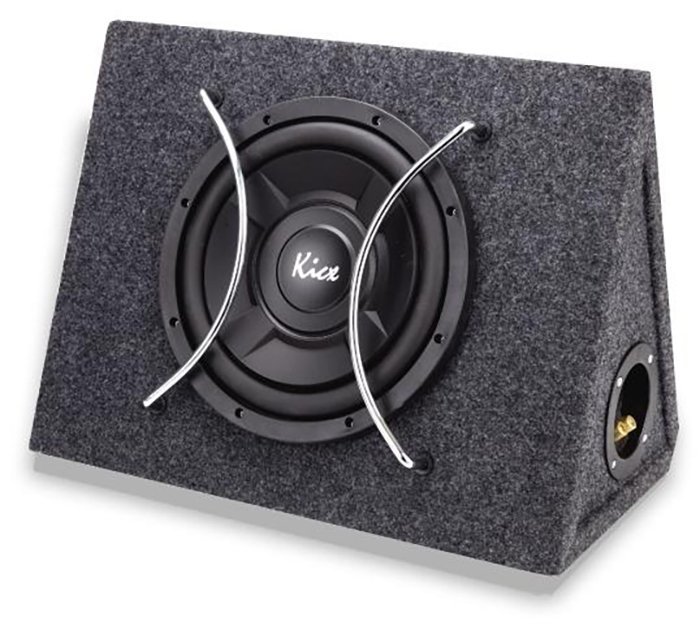

This is the easiest type of housing for a speaker system to produce. The oscillation in such a case is in a closed volume and is finally extinguished. But since a sound wave is a kind of energetic force, it becomes warm when attenuated. Despite the fact that the amount of this heat is small, it still has some effect on the parameters of the acoustic system (when the air becomes warm, the system expands and stiffens). In order to prevent such an effect, a closed box is filled from the inside with a special sound absorber, which is not only able to absorb sound, but also heat. The temperature rises much less and the dynamics "seem" that behind him there is a lot more volume than in reality. Practically, this method manages to increase the “acoustic” volume of the box, in comparison with the geometric, by 15-20 percent.
Despite the simplicity of the design, such a system has many advantages. First, the characteristics are calculated very simply, since there is only one parameter here-volume. Secondly, throughout the whole range, the oscillations of the frequencies of the diffuser are constrained by the elastic reaction of the air volume. This greatly reduces the likelihood that the speaker will be overloaded or mechanically damaged. Thirdly, with proper selection of the parameters of the head and volume, the closed box does not have its own characteristics in the impulse response, which to a large extent determine the subjective perception of the bass range.
But, if it were all so good, the need for other types of boxes would immediately disappear. The closed box has only one, but a very significant drawback-efficiency. A closed box has the lowest efficiency value in comparison with other types of acoustic design. If you take two boxes of different sizes with the same frequency range, the effectiveness of a smaller box will be worse.
Vented box
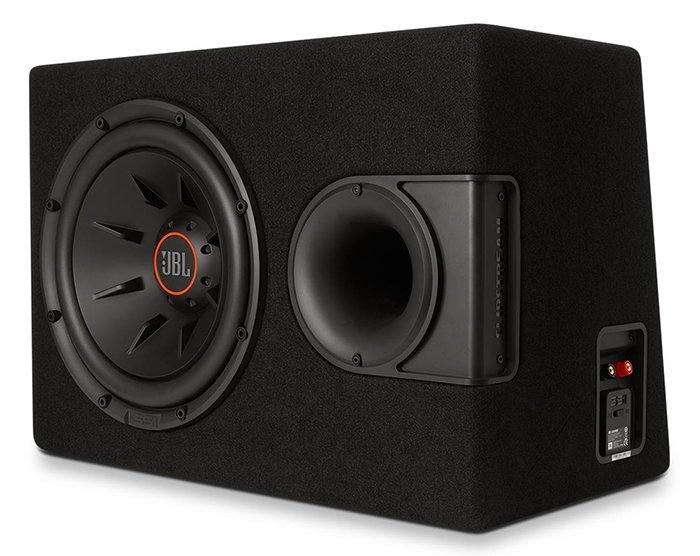

The next most popular design type is phase inverter. Such a housing is more responsive to the radiation of the back side of the diffuser. In a phase inverter, the proportion of energy that is “put against the wall” in a closed box is sent to a peaceful course. The volume inside is connected to the surrounding space in the tunnel, in which there is some air mass. The mass quantity values are chosen so that, in combination with the elasticity of the air inside the box, create another oscillation system that receives energy from the back side of the diffuser. The effect, which is obtained as a result, is achieved in a small frequency range (no more than two octaves), but within these frequencies the efficiency increases significantly.
In addition to high efficiency, the phase inverter has another important advantage-near the tuning frequency, the amplitude of oscillation of the diffuser is significantly reduced. At first glance, this may seem like a paradox, since the presence of a huge hole in the loudspeaker housing can hold the movement of the diffuser, but still it is a fact. In its working range, the phase inverter generates practically greenhouse conditions for the speaker. It can be said for sure that at the tuning frequency the amplitude of oscillations is small, and most of the sound is emitted by the tunnel. The input power, which is allowed, is maximum here, and the distortions that the speaker introduces are, on the contrary, insignificant.
Above the tuning frequency, the tunnel is becoming less and less “transparent” for sound vibrations. Due to the inertia that lies within its air mass, the loudspeaker functions as closed. Below the tuning frequency, the opposite happens: the inertia of the tunnel gradually goes away and at minimum frequencies the speaker works almost without load, as if it was removed from the housing. The amplitude of oscillations at high speeds increases, and with it the risk of falling off the diffuser or breakdown of the voice coil from an impact near the magnet. In general, if not protected, the possibility of buying a new speaker will become a harsh reality.
In order to avoid such problems, in addition to careful selection of the volume level of the sound, you need to use infra-low frequency filters. By removing a part of the spectrum where there is no useful signal (less than 25-30 Hz), such filters do not allow the diffuser to go into separation with danger to their own lives and the user's wallet.
A phase inverter is very capricious of choosing parameters and settings, since for a particular speaker there are already three parameters-this is the volume of the box, its cross section and, of course, the length of the tunnel. The tunnel itself is often done in such a way that the length of the tunnel can be coordinated in the finished subwoofer by changing the tuning frequency.
Bandpass
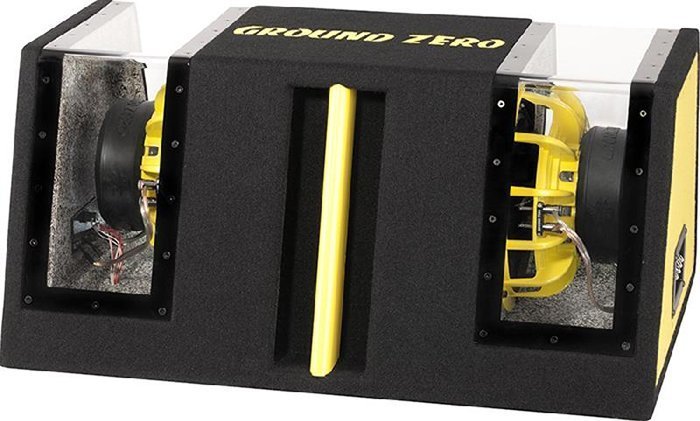

The third, last, type of subwoofer, which is often used in cars (although least often) is a loudspeaker. If the phase inverter and the closed box are acoustic high-pass filters, the band pass combines high-pass and low-pass filters. The simplest way loudspeaker is a fourth-order single loudspeaker (single vented). It is a closed volume of the rear and anterior chamber. The speaker is mounted in the partition between these chambers so that both sides of the diffuser work on fully or partially closed volumes. From this and took the term "symmetrical load."
Of all the popular designs, the loudspeaker is most effective. Moreover, its effectiveness is directly related to the bandwidth, more precisely, with its width. The frequency response of a loudspeaker is similar to a bell. By selecting the appropriate volume and frequency settings of the front camera, you can make a subwoofer with a fairly wide bandwidth, but with limited impact. The bell can be low and wide, but you can make it with a narrow band and very high efficiency in such a band. With all this, the bell will stretch upwards.
Bandpass is a rather capricious case in the calculation and the most time-consuming in production. Since the speaker of such a case is buried deep inside, it is necessary to assemble the box in such a way that the removable panel does not violate the rigidity and tightness of this design. Impulse characteristics are also not the best indicator, especially with a wide band.
These disadvantages are primarily compensated for by high efficiency, as well as by the fact that all the sound passes through the tunnel, and the speaker is completely closed. When compiling such a subwoofer, there are many possibilities for installing it in a machine. It is enough to find a small place between the luggage compartment and the cabin where the tunnel mouth can fit.
Watch car subwoofer video reviews
Materials on the topic
Car subwoofers: Best Sellers

Stay tuned for updates!
Subscribe to our Telegram channel and be the first to receive useful materials.
Subscribe