How to choose a UPS (uninterruptible power supply)?

To understand all the advantages of a device, you need to get a clear idea about it. Therefore, we decided to tell you simply and intelligibly what an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is, what it is for, how to choose a UPS (for a computer, office, home, boiler, circulation pump, compressor and other equipment).
What is a UPS and what is it for?

An uninterruptible power supply (UPS, UPS - Uninterruptible Power Supply) is a secondary power supply designed to supply power during a short-term outage of the main power source, as well as to protect against existing interference in the network while maintaining acceptable parameters for the main source network - such description provided by GOST.
In simple terms, it is able to power (thanks to the battery) the equipment connected to it when the mains power is interrupted, and switch to battery operation without harm to the equipment, in addition, when using a UPS with automatic volt regulation, there is protection against surges voltage.
Rolling blackouts have recently made UPS even more relevant, as well as regular planned and unplanned power outages. It is much more rational to “protect” your equipment through this device than to face its failure.
What are UPS types?

The most common type is linear interactive, they are presented in two forms:
- with an approximated sinusoid;
- with a fully sinusoidal output voltage (correct sine wave).
This type is equipped with a switching device that switches the system from mains power to battery backup in 2-4 ms. In addition, there is an automatic voltage regulator (AVR) - it serves as a stepped stabilizer.
How to choose a UPS?
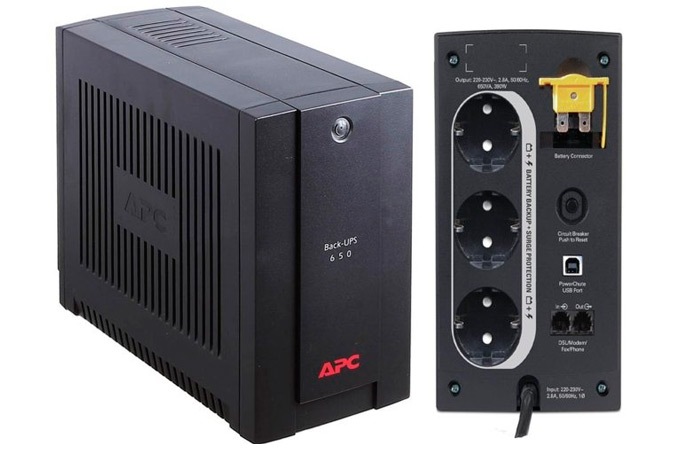

All linear-interactive uninterruptible power supplies with an approximate sine wave are suitable for switching power supplies, and UPS with a regular sine wave are universal, so for consumers with transformer power supplies (compressor, refrigerator), you need to use them.
The choice of a UPS is actually not too difficult, you just need to know the parameters that will be required for this. There are many tables that themselves carry out the calculation based on the specified parameters.
You need to know the total power (W) of the equipment, plus, importantly, pay attention to the starting currents of the equipment, because. they can be several times higher than with the constant consumption of the device, in which case it is worth adding 200-300% to the power of the equipment. You also need to understand how much battery life is required. Based on this, it is worth choosing a UPS.
The location of the battery (battery) can be internal (pre-installed by the manufacturer) and external (replaceable, selectable batteries), that is, in theory, there are various configuration options.
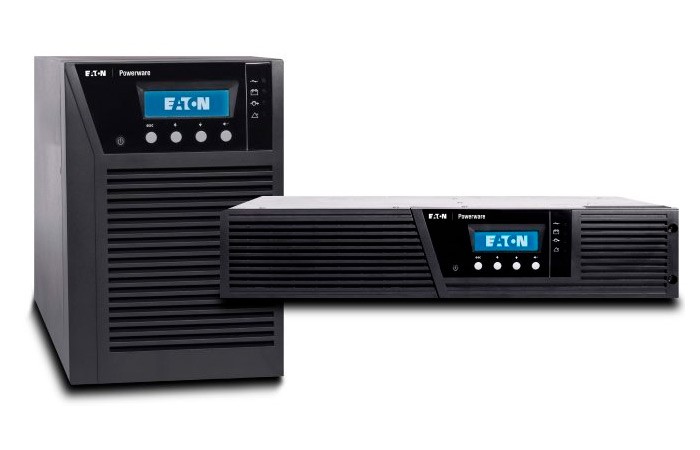

In practice, most often in UPS with an approximate sine wave (sometimes they are simply called "computer UPS"), they are produced with internal pre-installed batteries, and for UPS with a regular sine wave, models with external (remote) batteries are most in demand.
It is "computer UPS" that is perfect for office equipment, because. these models are: ergonomic, compact, have a minimum of external components and wires.
A small box will not interfere and will cope with the task - it will be possible to successfully and without loss complete the session without losing important information in the PC. Battery life is fixed, tk. The battery capacity is limited, but it is enough to complete the processes.
But models with the correct sine wave with externally connected batteries are suitable for equipment with any type of power supply. Thanks to replaceable batteries, battery life is selected individually.
Depending on the voltage (V) of the UPS, multiple batteries can be connected. What does it mean? If the UPS is 12V, it will be correct to connect only one 12V battery to it, and if it is 24V, then you already need to connect two 12V batteries, which will give a total voltage of 24V, also 48V - there are already 4 12V batteries in parallel to them.
The battery capacity (Ah) determines the battery life of the UPS, as well as the price of the battery, so you need to focus on the ratio of the cost of the battery and the required margin of time.
On the types of batteries, their pros and cons, you can learn very soon, in future articles.
When the choice of an uninterruptible power supply is made, it remains to connect it correctly. There are sockets on the back or side wall of the UPS, in which equipment is connected, as in a regular surge protector, and the UPS itself is connected to the network. Before connecting, if the battery is external, it is correct to connect the battery first (clear color coding "black to black", "red to red" minimizes the possibility of error).
An uninterruptible power supply is NOT required for: boiler, iron, electric kettle, oil cooler.
Having this information, you can correctly select from all your electrical appliances exactly those that need an uninterruptible power supply and not overpay when buying. A surge protector is suitable for such equipment - an extension cord that can be disconnected from the network with a fuse if the voltage has increased unacceptably. This solution is the most budgetary, it is suitable for equipment in which the safety of data or additional battery life without power supply is not important.
Conclusion
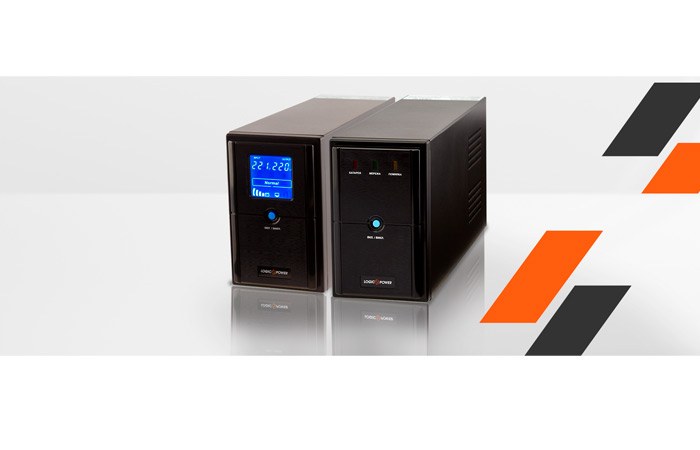

1. A UPS with an approximate sine wave is only suitable for switching power supplies.
Pros: Compactness, relatively low price;
Cons: fixed battery life, because the model is selected in a certain capacitive parameter.
2. A UPS with a correct sine wave is universal.
Pros: the possibility of individual selection of battery life;
Cons: relatively large dimensions (due to external battery connection).
3. To select a UPS and a battery, clear parameters are required: the total power of the equipment (W), the desired requirement for autonomous operation. As well as taking into account the starting currents of the equipment.
You can choose and you can buy an uninterruptible power supply at 130.com.ua with delivery in Ukraine.
Related materials
Inverters, voltage converters: Best Sellers

Stay tuned for updates!
Subscribe to our Telegram channel and be the first to receive useful materials.
Subscribe